How to Use Helical Ground Anchors for Reliable Ground Support Systems
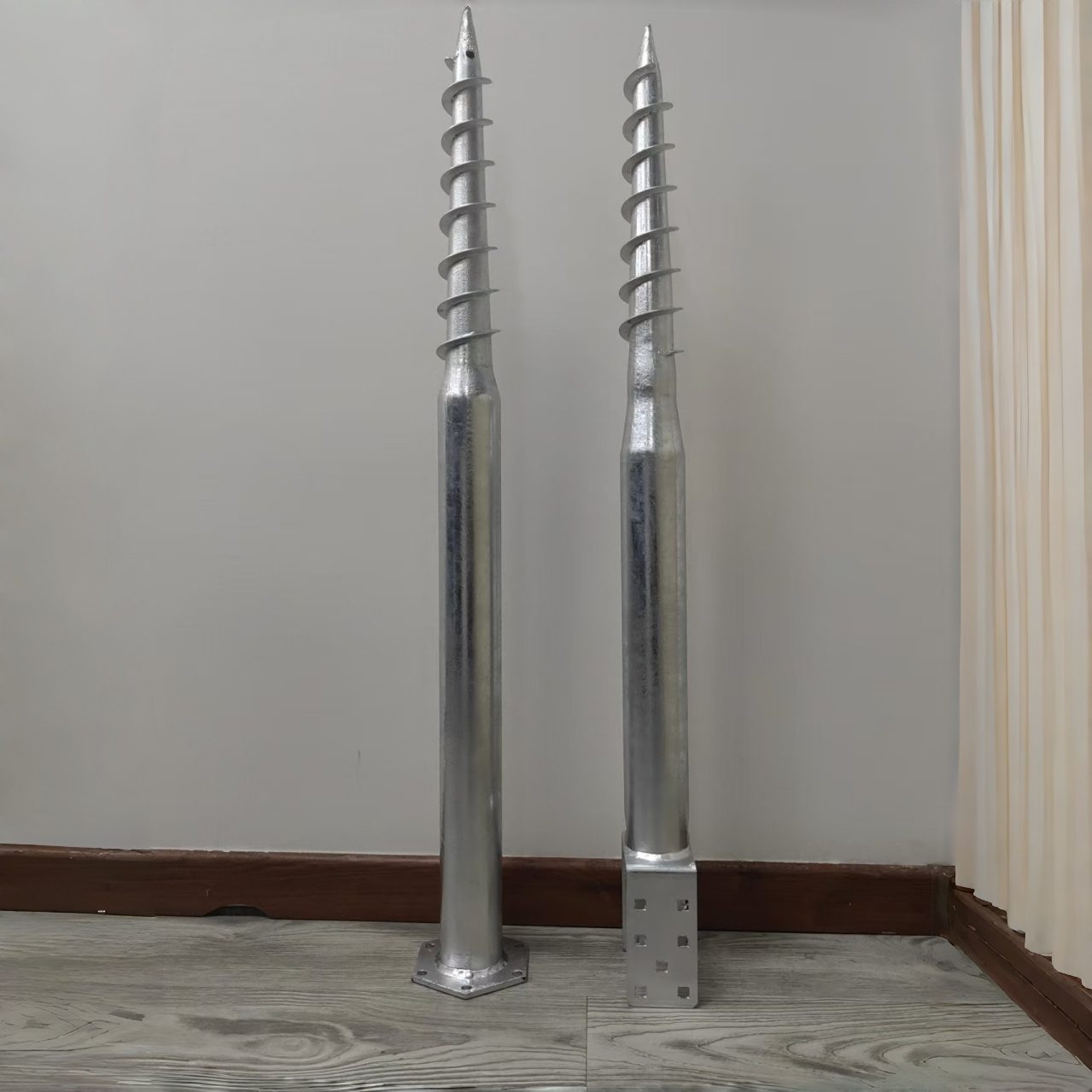

Understanding Helical Ground Anchors and Their Applications
Ground screws are shifting from specialized uses to widespread adoption. Builders prefer them for quicker, neater, and more flexible base systems. Helical Ground Anchors, also called screw foundation anchors, play a key role in today’s building projects. They offer great flexibility, simple handling, and eco-friendliness. These anchors work well in short-term and long-term setups. You can find them in large solar fields and EV charging points. They also suit home decks and public works.
In big solar projects, ground screws let developers stick to timelines and limit ground disturbance. They prove especially useful in home-based garden setups, fences, and prefab structures. Traditional concrete bases often don’t fit these needs well.
Key Components of a Helical Ground Anchor System
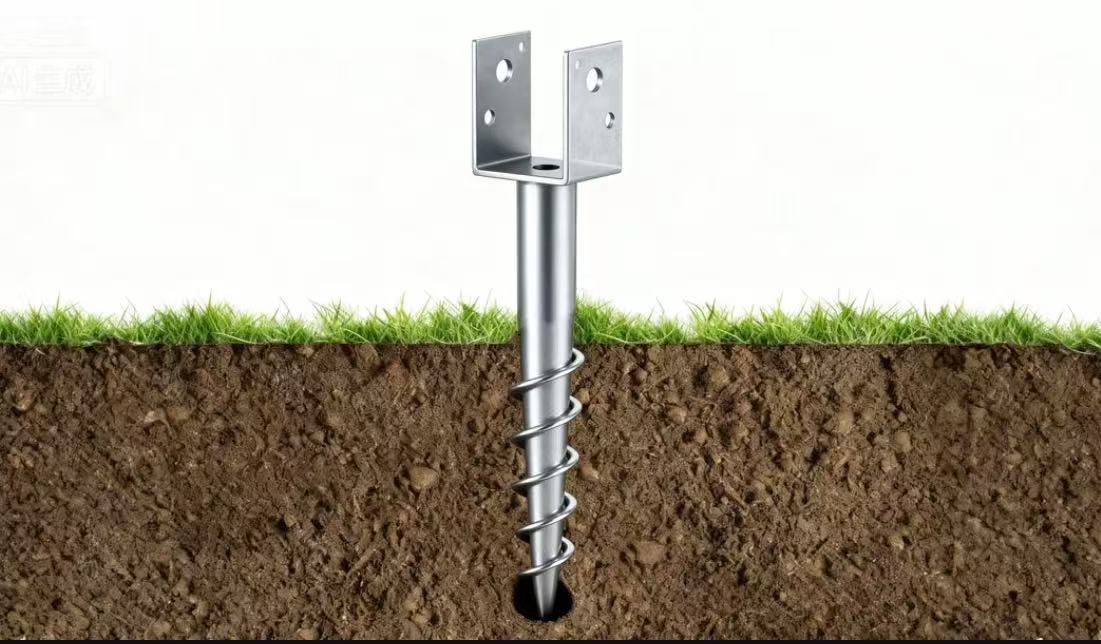
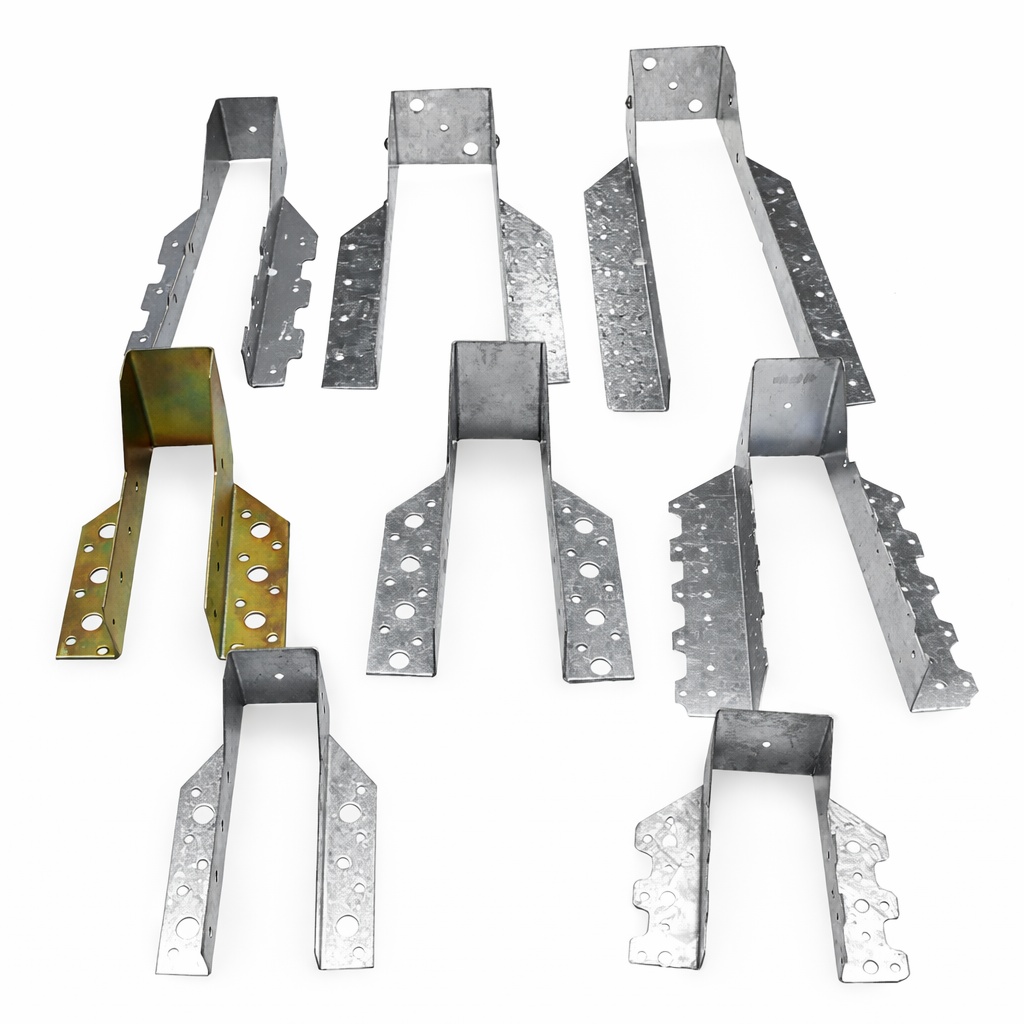
A helical ground anchor system usually contains these main parts:
-
Helical blade or screw flights:These let the anchor twist into the earth with little soil shifting. In straight M-type designs, such as M68×120×1200 mm, the threaded section helps the anchor advance smoothly into the soil.
-
Central shaft: It moves weight from the building to the ground below. For example, models with a defined 400 mm thread length support stable load transfer in common ground conditions.
-
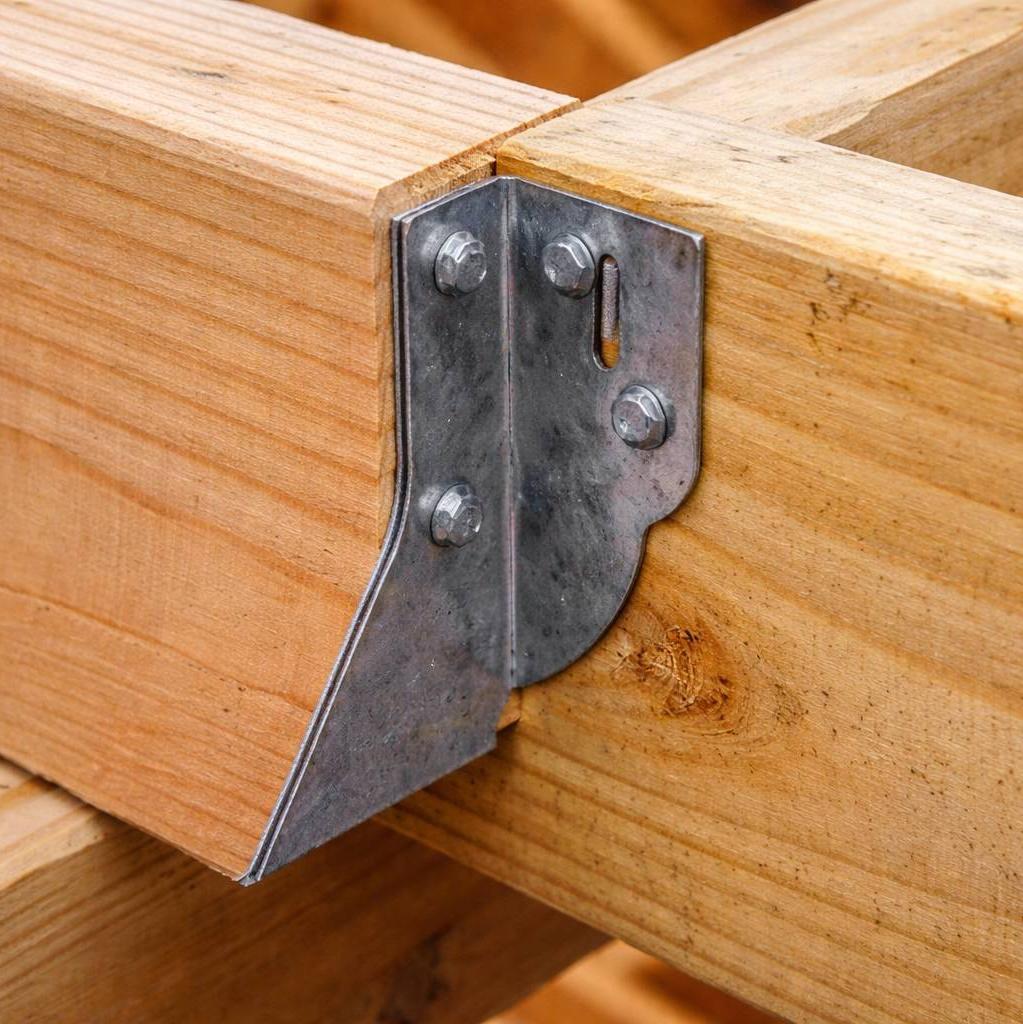
Anchor head or connection bracket: This links to different upper parts like posts, beams, or supports. U-shaped anchors, such as U10×70×4×85×1000 mm, are often used where direct post or frame connections are required.
All components typically feature hot-dip galvanized finishes to improve resistance to corrosion in underground and outdoor environments.

Benefits of Using Screw Foundation Anchors for Ground Support
Screw Foundation Anchors cover items like ground screws, driven piles, U-type anchors, and flange bases. These gain popularity because of fast setup, ability to reuse, and low harm to the environment. Other advantages include these points:
-
No concrete required: This cuts down wait time for drying and keeps the site tidy.
-
Immediate load-bearing: Perfect for projects that need speed.
-
Eco-friendly: Little soil upset, and they can be used again.
-
Versatile applications: Suitable for garden sheds to road signs.
Site Evaluation Before Installing Helical Ground Anchors
Good site checks matter a lot. Key things to look at include:
-
Soil type and density
-
Water table depth
-
Load requirements
-
Slope angles
In one job in Gdańsk, Poland, workers set up a 4×3m shed on uneven land. The ground had a 40cm drop in height. No concrete or big digging was needed. This example highlights how well these anchors perform when you understand the site properly.
Step-by-Step Guide to Installing a Helical Ground Anchor
-
Site marking: Outline where anchors go using basic layout gear.
-
Pilot hole (if needed): Drill a starter in tough or packed soils.
-
Anchor driving: Twist the anchor into the earth with a torque tool or small rotary device.
-
Depth control: Make sure it hits the firm ground layer that holds weight.
-
Attachment: Link building parts using brackets or post holders.
You can finish testing and marking in just one day. This holds true even for decks with many anchor spots.
Tools and Equipment Required for Screw Foundation Anchor Installation
The choice of tools depends on project size and ground conditions. Common options are:
| Tool Type | Usage |
|---|---|
| Manual driving rod | For small DIY applications |
| Electric torque driver | For medium-sized residential installations |
| Hydraulic rig | For commercial or heavy-duty applications |
| Torque meter | To ensure proper depth and load compliance |
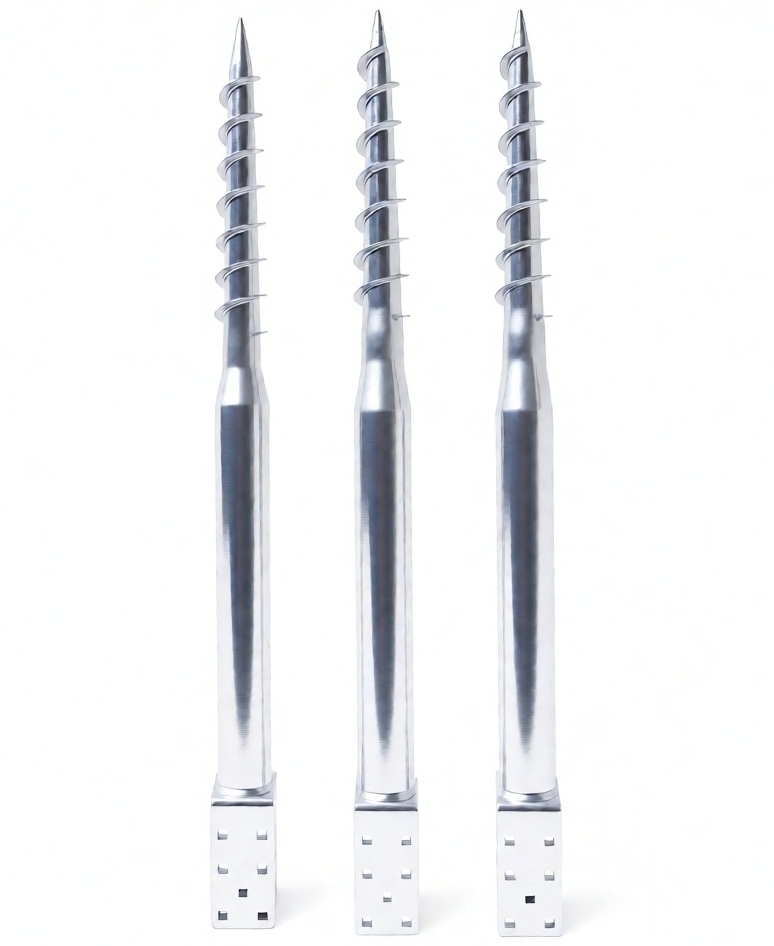

Factors Affecting the Load Capacity of Helical Ground Anchors
Several key factors determine the load capacity of helical ground anchors, including anchor diameter and length, blade size and pitch, soil bearing capacity, and the installation torque applied.
In general, larger and heavier anchor designs are capable of handling higher loads. For example, the M160×8/7×1600×3.0 mm screw anchor, with a unit weight of 10.78 kg, is designed for high-load applications requiring strong ground resistance.
By contrast, smaller configurations such as U-shaped anchors measuring 81×685×1.8 mm are intended for lighter-duty uses, including yard fencing and similar surface installations.
Common Mistakes to Avoid During Installation
-
Incorrect depth measurement: This causes weak holding power.
-
Improper alignment: It harms the build’s strength.
-
Skipping soil tests: Raises the chances of anchor issues.
-
Over-torquing: Might harm the threads or lessen grip.
-
Using incompatible brackets: Could lead to shaky links.
To reduce these risks, installers should follow clear installation guidelines and select connector components that are properly matched to the application and load requirements.
Maintenance and Inspection Practices for Long-Term Stability
Steady checks help keep things solid over time:
-
Look for rust or wear, particularly near the sea.
-
Confirm that joints stay firm.
-
Examine straightness from time to time.
-
Add rust-fighting grease to screws and nuts when necessary.
Comparing Helical Ground Anchors with Other Ground Support Methods
| Feature | Helical Anchors | Concrete Foundations |
|---|---|---|
| Installation Time | Hours | Days |
| Environmental Impact | Low (no excavation) | High (soil sealing) |
| Reusability | Yes | No |
| Load Readiness | Immediate | Requires curing |
| Equipment Needed | Minimal to Moderate | Heavy |
| Cost Efficiency (overall) | High | Moderate to High |
Spiral ground anchors beats traditional concrete bases in many ways. Ground piles go straight into the soil without digging. This boosts overall efficiency greatly.
STRZ integrates advanced surface coatings, flexible sizing options, and customized solutions to meet varying soil conditions and project requirements. Committed to high manufacturing standards and reliable service, we delivers durable screw foundation anchor systems trusted across residential, industrial, and renewable energy projects worldwide.
FAQ
Q: How deep should I install a helical ground anchor?
A: Depth varies by weight needs and ground state. Anchors must reach a steady soil layer that handles the needed pull or push forces.
Q: Can I install a helical ground anchor myself?
A: Yes, particularly for home projects like decks or garden spaces. STRZ makes products that work with hand tools or small electric drivers.
Q: What type of soil is suitable for screw foundation anchors?
A: These anchors do fine in sandy, clay-like, or blended soils. In rocky spots, you might need to drill first.
Q: Are STRZ’s ground screws corrosion-resistant?
A: Yes. STRZ’s ground screws use hot-dip galvanizing or penetration galvanizing with salt spray resistance up to 400 hours.
Q: Can I order customized helical anchors for unique projects?
A: Absolutely. STRZ supports customized specifications, including length, diameter, thread pitch, and surface treatment to meet project-specific demands.